Explain How Different Types of Fatty Acids Affect Cardiovascular Disease
In the last decade it is increasingly recognized that the very long chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids n-3 FA can. Liquid chelation is the key to absorption and lowering Plaque in the Blood vessels.
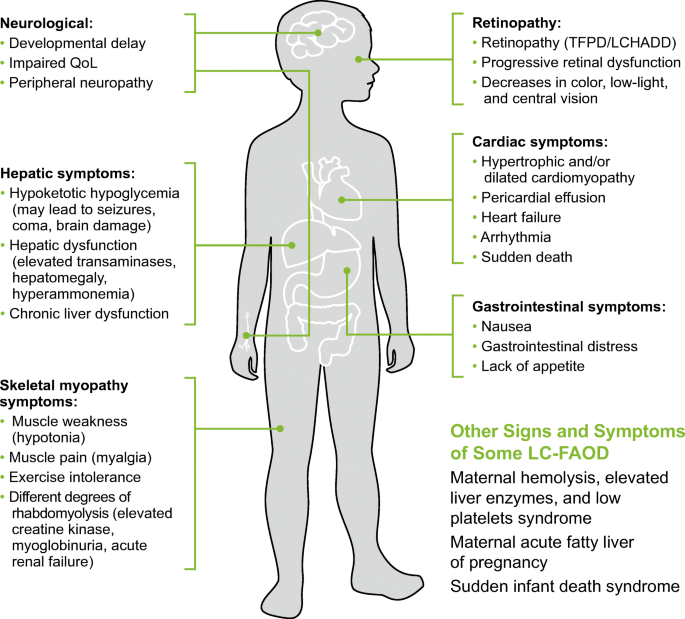
Clinical Manifestations And Management Of Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Springerlink
Since the early 1970s and thereafter long-chain omega n-3 PUFA notably eicosapentaenoic acid EPA and docosahexaenoic acid.

. The opposite is true when eating more polyunsaturated fatty acids which include omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. 1 22 Nutrition and modification of diet make. Also dietary recommendations for cis-MUFA as derived by various organizations are not in agreement.
Fats and cholesterol can affect blood cholesterol levels. Furthermore increased intake of cholesterol saturated and trans fatty acids has been linked to the development of several cardiovascular diseases. There are three types of fat.
How do trans fats affect my health. Scientists regulators and communicators have described the biological effects and the health impacts of fatty acids. Although traditionally most interest in the health impact of fatty acids related to cardiovascular disease it is now clear that fatty acids influence a range of other diseases including metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes inflammatory diseases and cancer.
Dairy fat and its cardiovascular impact are being evaluated. Ad Help for People w Heart Disease and High LDL-C Despite Statin. Its also associated with a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Moderate evidence indicates that total intake of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids particularly eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid from food sources by adults is associated with lower risk of cardiovascular disease. A Group Of Rare Autosomal Recessive Disorders. The epidemiological association between high intakes of n-3 fatty acids FA and decreased morbidity and mortality from cardiovascular disease CVD can be explained by two main basic mechanisms.
This report summarizes our current understanding of how monounsaturated fatty acids MUFAs affect risk for cardiovascular disease CVD. Eating trans fats increases your risk of developing heart disease and stroke. Different saturated fatty acids have varying effects on LDL cholesterol HDL cholesterol and the TCHDL cholesterol ratio when they replace carbohydrate.
An elevated blood cholesterol level is a risk factor for heart disease. Discover How Certain Lifestyle Factors Can Affect High Bad Cholesterol And Lead To ASCVD. They also looked at how omega-3 fatty acids affect longer term cardiovascular problems such as the risk of heart attack heart failure stroke death from heart disease and death from any cause.
Saturated monounsaturated and polyunsaturated. Researchers looked at how omega-3 fatty acids from food and dietary supplements affect cholesterol and triglyceride levels and blood pressure. This is a topic that has attracted considerable scientific interest 1 2 3 in large part because of uncertainty regarding whether MUFA or carbohydrate should be substituted for saturated fatty acids SFAs and the desirable.
A an effect on atherothrombosis and b an effect on cardiac arrhythmias. Overview on Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease. The longer chain stearic acid 180 has been shown to have no effect on LDL or HDL cholesterol or the TCHDL cholesterol ratio and saturated fatty acids of shorter length have been shown to have a greater.
Download The Free Comprehensive Heart Disease Treatment Guide. Ad Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders. The amounts types and family history are the key.
1 52 CHD is the number one cause of death in the USA accounts for approximately 17 of deaths and is associated with over 1 million myocardial infarctions MIs each year. Like monounsaturated fat polyunsaturated fat can decrease your risk for heart disease by lowering blood cholesterol levels according to the American Heart Association. Learn About The Mechanism Of Disease Metabolic Decompensation.
The risk of coronary heart disease CHD associated with saturated fatty acids SFA varies from no association to a significantly important risk. Cardiovascular disease CVD is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in the world both in developed and developing countries. Doctors used to think that omega-6 fatty acids contributed to heart disease.
In contrast to the negative effects of LDL cholesterol saturated and trans fatty acids the intake of both monounsaturated and ω-3 and ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids is associated with anti-inflammatory effects. Ad You Can Have a Healthier Heart by Cleaning Arteries. Fats and cholesterol can help keep our bodies healthy or they can promote disease.
Results from observational studies have been consistent with these findings with several systematic reviews and meta-analyses showing that higher consumption of fish and higher dietary or plasma levels of omega-3s are associated with a lower risk of heart failure coronary disease and fatal coronary heart disease 4344. Ad Request a Consultation with a Specialist at Cleveland Clinic. This review examines the existing literature on the.
De Souza RJ Mente A Maroleanu A et al. The effects of cis-monounsaturated fatty acids cis-MUFAs on the risk of coronary heart disease CHD and on CHD mortality are not clear. Long chain fatty acids LCFA contain 13 or more carbons that can either be saturated or contain one or more double bonds.
These pathological conditions involve interactions between environmental genetic and epigenetic factors. Earlier studies have mainly focused on the effects of cis-MUFA on serum lipids and lipoproteins. Thus in recent years dietary recommendations have been made to decrease saturated and trans-fatty acids and to emphasize unsaturated fatty acids both monounsaturated MUFAs and polyunsaturated fatty acids PUFAs.
Omega-6 fatty acids are found in foods like leafy green vegetables seeds nuts and vegetable oils. Systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Intake of saturated and trans-unsaturated fatty acids and risk of mortality cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
These mechanisms probably reflect different beneficial influences of n-3 FA on cardiovascular biology. The omega-3 fatty acids are known to exert cardiovascular protective effects. Controversy surrounds omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids because even though they lower LDL cholesterol levels excessive intakes do not appear to be correlated with cardiovascular benefit.
Medium chain fatty acids MCFA contain 712 saturated carbons while short chain fatty acids contain 1-6 saturated carbons. Recent advances in nutriepigenomics are contributing to clarify the role of some nutritional factors including. Diet can affect the majority of modifiable risk factors for CVD.
Most Americans eat too much fat. Chronic illnesses like obesity type 2 diabetes T2D and cardiovascular diseases are worldwide major causes of morbidity and mortality. Trans fats raise your bad LDL cholesterol levels and lower your good HDL cholesterol levels.
Such as the access to different types of fat says co-author Simon N.
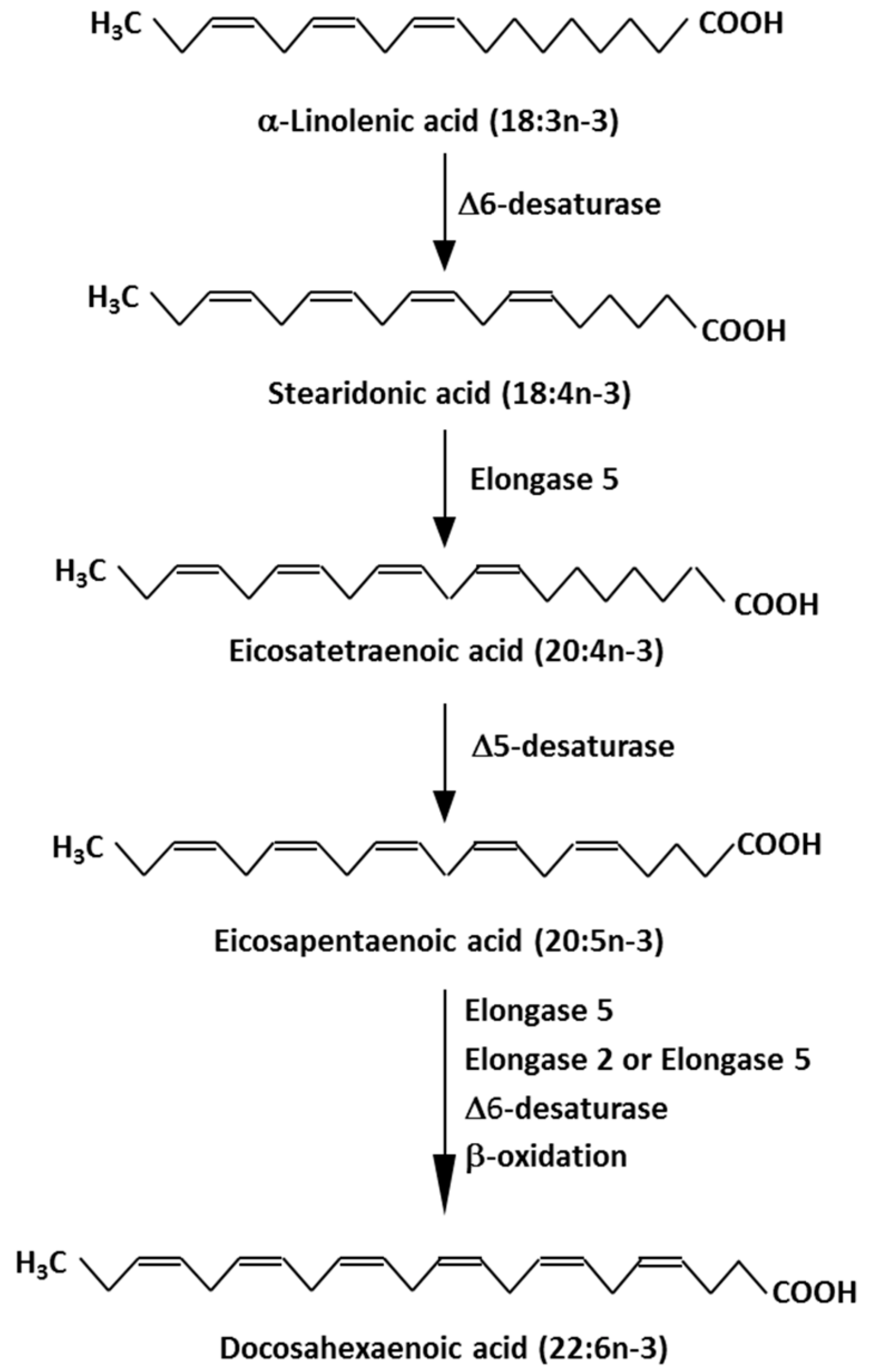
Ijms Free Full Text Marine Omega 3 N 3 Fatty Acids For Cardiovascular Health An Update For 2020 Html

No comments for "Explain How Different Types of Fatty Acids Affect Cardiovascular Disease"
Post a Comment